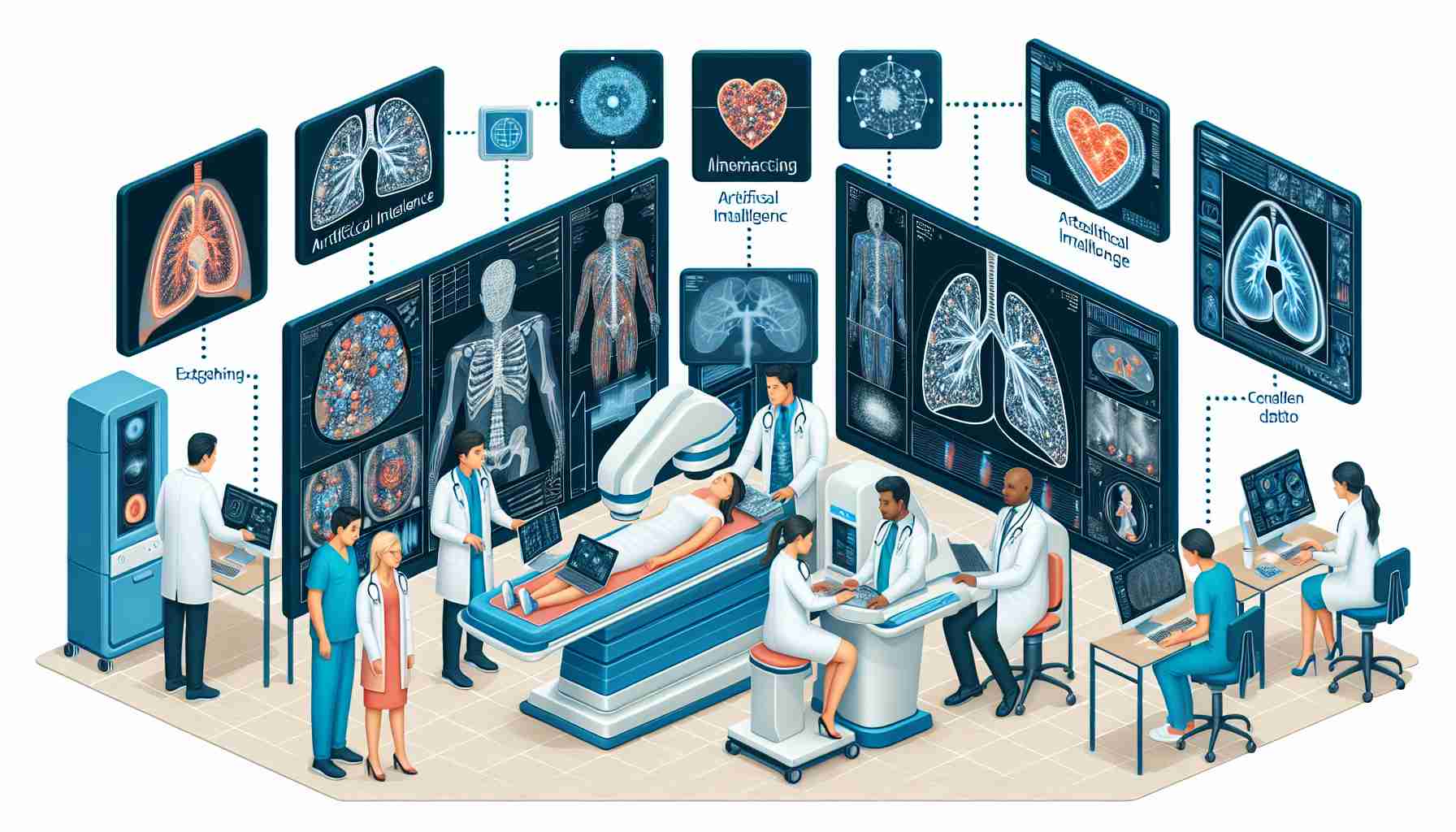
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into medical imaging devices, such as MRI machines, is becoming increasingly prevalent in the healthcare sector. Illustrating this advancement is Canon Medical Systems, which has adopted AI for brain imaging diagnostics, as observed in recent images captured on the 12th in Yokohama City.
Medical professionals are welcoming AI’s ability to enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Using sophisticated algorithms, the technology can process complex medical images, highlight potential issues, and support radiologists in making more informed decisions. This compliments the existing suite of tools and lends a transformative edge to patient care.
AI’s prowess in recognizing patterns imperceptible to the human eye marks a significant step forward in medical diagnostics. It’s not just about augmenting the processes; AI proposes a paradigm shift in healthcare, introducing unprecedented precision and a proactive approach to disease management.
As the technology matures and becomes more integrated into various diagnostic equipment, the potential for improved outcomes and streamlined workflows in hospitals and clinics is promising. The rise of AI in medical imaging is not just a fleeting trend but heralds a new era in the evolution of healthcare technology.
Important Questions and Answers:
1. What types of medical imaging can AI be integrated with? AI is not limited to one type of medical imaging; it can be integrated with various modalities including MRI, CT scans, X-rays, ultrasound, and PET scans. AI technologies applied to these different modalities help in detecting abnormalities, quantifying physiological functions, and even predicting patient outcomes based on the images.
2. How does AI improve the accuracy of diagnoses in medical imaging? AI algorithms, especially deep learning models, are exceptionally good at identifying complex patterns in imaging data that may be too subtle for the human eye to detect. By learning from vast amounts of historical imaging data, AI can assist radiologists by flagging areas of interest, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnosis or overlooked conditions.
3. Is there resistance to the adoption of AI in medical imaging? Despite its benefits, there can be skepticism or resistance among healthcare professionals due to concerns over job displacement, over-reliance on technology, or a lack of understanding of AI capabilities. Ensuring that AI acts as an assistive tool rather than a replacement is vital for broader acceptance.
Key Challenges and Controversies:
– Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI necessitates the processing of large amounts of sensitive patient data, posing significant challenges in ensuring privacy and security compliance, such as with HIPAA in the United States.
– Algorithm Bias: AI systems can perpetuate biases present in the training data, leading to disparities in healthcare quality among different population groups. Ensuring diverse and representative datasets is crucial to mitigate this issue.
– Regulatory Hurdles: The regulatory landscape for AI in healthcare is complex. Efficient and thorough approval processes are needed to ensure patient safety without stifling innovation.
– Integration into Clinical Workflows: Successful deployment of AI tools requires seamless integration into existing healthcare IT systems and workflows, which can be challenging and costly.
Advantages: AI in medical imaging offers various benefits, such as increased efficiency, reduced scan times, enhanced diagnostic accuracy, and improved patient outcomes. It enables early disease detection and more personalized treatment plans.
Disadvantages: Potential drawbacks include the initial high cost of implementation, the need for specialized training for healthcare professionals, and the previously mentioned challenges of data privacy, algorithm bias, and integration into clinical workflows. Additionally, there can be legal and ethical implications if AI makes incorrect recommendations leading to misdiagnosis.
For more information about AI technology in healthcare, please visit the following official links:
– National Institutes of Health (NIH): An agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the NIH provides information about health research, including the role of AI in medical imaging.
– World Health Organization (WHO): An international organization that provides leadership on global health matters and could have relevant resources on AI in healthcare.
– Radiological Society of North America (RSNA): An association of radiologists and related professionals that could have substantial resources and research papers on the topic of AI in medical imaging.
– U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA regulates medical devices and has guidelines and information on AI-driven medical imaging products.
The source of the article is from the blog elektrischnederland.nl